|
Africa
Africa is a
Continent not a Country
Africa is the
world's second-largest and second most-populous continent, after Asia. At about
30,221,532 km² (11,668,545 sq mi) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of
the Earth's total surface area, and 20.4% of the total land area. With more than
900 million people (as of 2005) in 61 territories, it accounts for about 14% of
the world's human population. The continent is surrounded by the Mediterranean
Sea to the north, the Suez Canal and the Red Sea to the northeast, the Indian
Ocean to the southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west.
Area: about 30 244 000
km2 (11 700 000 mi2) including its adjacent islands it
covers about 20 percent of Earth's total land area.
Coastline: 30,539 km 18,976 miles
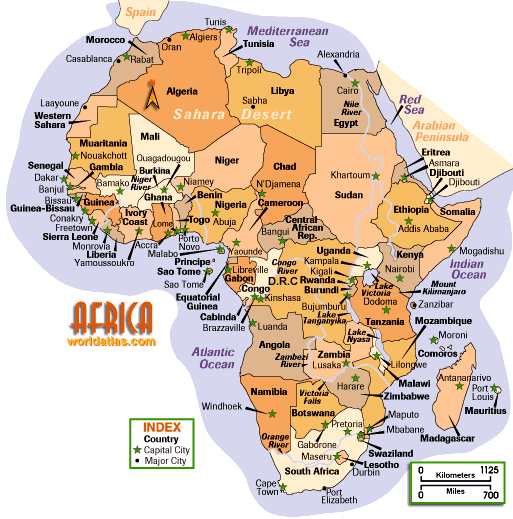
Population: 900
million human inhabitants, about 20 percent of the world's population.
Highest Point: Mount Kilimanjaro - Uhuru Peak on the volcano Kibo, 5,895
m (19 340 ft) in Tanzania.
Largest Lake: Lake Victoria or Victoria Nyanza; 68 870 sq. km.
Longest River: Nile; 6 695 km.
Languages of Africa: about thousand languages classified in four major
language families:
Afro-Asiatic (e.g. Berber lang), Nilo-Saharan, Niger-Congo (Bantu), and
Khoi-San.
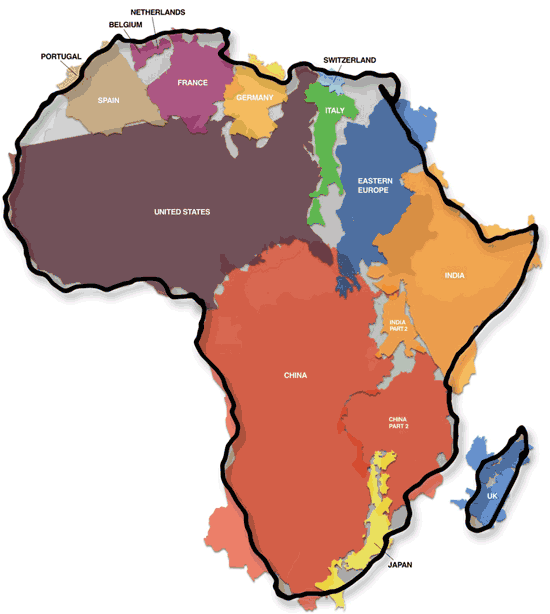
|
Country |
Capital City |
|
Nigeria
|
Abuja
|
|
Egypt
|
Cairo
|
|
Ethiopia
|
Addis Ababa
|
|
Congo-Kinshasa
|
Brazzaville
|
|
South Africa
|
Pretoria
|
|
Sudan
|
Khartoum
|
|
Tanzania
|
DaresSalaam
|
|
Kenya
|
Nairobi
|
|
Morocco
|
Rabat
|
|
Algeria
|
Algiers
|
|
Uganda
|
Kampala
|
|
Ghana
|
Accra
|
|
Mozambique
|
Maputo
|
|
Madagascar
|
Antananarivo
|
|
Côte d'Ivoire
|
Yamoussoukro
|
|
Cameroon
|
Yaoundé
|
|
Burkina Faso
|
Ouagadougou
|
|
Zimbabwe
|
Harare
|
|
Malawi
|
Lilongwe
|
|
Mali
|
Bamako
|
|
Senegal
|
Dakar
|
|
Malawi
|
Lilongwe
|
|
Niger
|
Niamey
|
|
Angola
|
Luanda
|
|
Zambia
|
Lusaka
|
|
Tunisia
|
Tunis
|
|
Chad
|
N'Djamena
|
|
Guinea
|
Conakry
|
|
Somalia
|
Mogadishu
|
|
Rwanda
|
Kigali
|
|
Burundi
|
Bujumbura
|
|
Benin
|
Porto-Novo
|
|
Burundi
|
Bujumbura
|
|
Sierra Leone
|
Freetown
|
|
Libya
|
Tripoli
|
|
Togo
|
Lomé
|
|
Eritrea
|
Asmara
|
|
Central African Republic
|
Bangui
|
|
Congo-Brazzaville
|
Kinshasa
|
|
Mauritania
|
Nouakchott
|
|
Liberia
|
Monrovia
|
|
Mauritania
|
Nouakchott
|
|
Namibia
|
Windhoek
|
|
Lesotho
|
Maseru
|
|
Gambia
|
Banjul
|
|
Botswana
|
Gaborone
|
|
Guinea-Bissau
|
Bissau
|
|
Gabon
|
Libreville
|
|
Mauritius
|
Port Louis
|
|
Swaziland
|
Mbabane
|
|
Comoros
|
Moroni
|
|
Equatorial Guinea
|
Malabo
|
|
Djibouti
|
Djibouti
|
|
Cape Verde
|
Praia
|
|
Western Sahara
Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
|
|
|
São Tomé and Príncipe
|
Sao Tome
|
|
Seychelles
|
Victoria
|
|
Saint Helena |
Jamestown |

|
Country |
Official and national Languages |
Other
spoken Languages
|
| Algeria |
Arabic |
French,
Berber dialects. |
| Angola |
Portuguese |
Narrow Bantu like Umbundu
and other African languages. |
|
Benin |
French |
Fon and
Yoruba (most common vernaculars in south), tribal languages (at least six
major ones in north). |
| Botswana |
English |
Setswana |
|
Burkina Faso |
French |
Native
African languages belonging to Sudanic family spoken by 90% of the
population. |
| Burundi |
Kirundi,
French |
Swahili (along Lake
Tanganyika and in the Bujumbura area). |
|
Cameroon |
English, French |
24
major African language groups. |
| Cape Verde |
Portuguese |
Kabuverdianu (Crioulo) (a
blend of Portuguese and West African words). |
| Central
African Republic |
French,
Sangho (lingua franca and national language) |
Banda, Gbaya and other tribal languages. |
| Chad |
French,
Arabic |
Sara (in south), more
than 120 different languages and dialects. |
Comoros
|
Arabic,
French |
Shikomoro (a blend of Swahili and Arabic). |
| Democratic Republic of
the Congo |
French |
Lingala (a lingua franca
trade language), Kingwana (a dialect of Kiswahili or Swahili), Kikongo,
Tshiluba. |
|
Congo, Republic of the |
French |
Lingala
and Monokutuba (lingua franca trade languages), many local languages and
dialects (of which Kikongo is the most widespread). |
| Côte
d'Ivoire |
French |
60 native dialects with
Dioula the most widely spoken. |
|
Djibouti |
French,
Arabic |
Somali,
Afar |
| Egypt |
Arabic |
English and French widely
understood by educated classes. |
|
Equatorial Guinea |
Spanish, French |
pidgin English, Fang, Bubi, Ibo. |
| Eritrea |
Tigrinya
(Tigrigna), Arabic, English |
Tigré (second major
language), Afar, Bedawi, Kunama, other Cushitic languages. |
|
Ethiopia |
Amharic |
Tigrinya, Oromo, Gurage, Somali, Arabic, 80 other local languages, English
(major foreign language taught in schools) |
| Gabon |
French |
Bantu languages like
Fang, Myene, Nzebi, Bapounou/Eschira, Bandjabi. |
|
Gambia, The |
English |
Mandinka, Wolof, Fula, other indigenous vernaculars. |
| Ghana |
English |
African languages
(including Akan, Moshi-Dagomba, Ewe, and Ga) |
|
Guinea |
French (spoken by 15-20%) |
Eight
national languages, Soussou (Susu, in coastal Guinea), Peulh (Fulani, in
Northrn Guinea), Maninka (Upper Guinea), Kissi (Kissidougou Region), Toma
and Guerze (Kpelle) in rain forest Guinea; plus various ethnic groups with
their own language. |
|
Guinea-Bissau |
Portuguese |
Crioulo (a mixture of
Portuguese and African), other African languages. |
| Kenya |
English, Kiswahili |
numerous indigenous languages. |
| Lesotho |
Sesotho (southern Sotho),
English |
Zulu, Xhosa. |
|
Liberia |
English 20% |
some 20
ethnic group languages, of which a few can be written and are used in
correspondence. |
| Libyan Arab Jamahiriya |
Arabic |
Italian, English, all are
widely understood in the major cities. |
|
Madagascar |
French,
Malagasy |
|
| Malawi |
English,
Nyanja (Chichewa, Chewa) |
Lomwe, Tumbuka, Yao,
other languages important regionally. |
|
Mali |
French |
Bambara
(Bamanakan), Arabic and numerous dialects of Dogoso, Fulfulde, Koyracini,
Senoufou, and Mandinka/Malinké (Maninkakan), Tamasheq are also widely
spoken. |
| Mauritania |
Arabic |
Hassaniya Arabic, Pulaar,
Soninke, Wolof, French |
|
Mauritius |
English, French |
Creole,
Hindi, Urdu, Hakka, Bhojpuri |
| Morocco |
Arabic |
Berber dialects, French
often the language of business, government, and diplomacy. |
|
Mozambique |
Portuguese (spoken by 27% of population as a second language) |
Makhuwa, Tsonga, Lomwe, Sena, numerous other indigenous languages. |
| Namibia |
English 7% |
Afrikaans common language
of most of the population and about 60% of the white population, German 32%,
indigenous languages: Oshivambo, Herero, Nama. |
| Niger |
French |
Hausa,
Djerma |
| Nigeria |
English |
Hausa, Yoruba, Igbo
(Ibo), Fulani, Ijaw, Ibibio and about 250 other indigenous languages spoken
by the different ethnic groups. |
| Réunion |
French |
Creole
widely used |
| Rwanda |
Rwanda (Kinyarwanda,
Bantu vernacular) French, English |
Kiswahili (Swahili) used
in commercial centers. |
| Saint
Helena |
English |
|
| Sao Tome and Principe |
Portuguese |
|
| Senegal |
French |
Wolof,
Pulaar, Jola, Mandinka |
| Seychelles |
English, French |
Creole |
|
Sierra Leone |
English (regular use limited to literate minority) |
Mende
(principal vernacular in the south), Temne (principal vernacular in the
north), Krio (English-based Creole a first language for 10% of the
population but understood by 95%) |
| Somalia |
Somali |
Arabic, Italian, English |
|
South Africa |
11 official languages, including Afrikaans, English, isiNdebele, Pedi,
Sesotho (Sotho), siSwati (Swazi), Xitsonga (Tsonga), Tswana, Tshivenda
(Venda), isiXhosa, isiZulu |
| Sudan |
Arabic |
Nubian, Ta Bedawie,
diverse dialects of Nilotic, Nilo-Hamitic, Sudanic languages, English. |
|
Swaziland |
English
(government business conducted in English), siSwati |
|
| Tanzania,
United Republic of |
Kiswahili (Swahili),
Kiunguju (name for Swahili in Zanzibar), English (primary language of
commerce, administration, and higher education) |
Arabic
(widely spoken in Zanzibar), Gogo, Haya, Makonde, Nyakyusa, Nyamwezi,
Sukuma, Tumbuka, many other local languages. |
|
Togo |
French (the language of commerce) |
Ewe and
Mina (the two major African languages in the south), Kabye (Kabiye) and
Dagomba (the two major African languages in the north) |
| Tunisia |
Arabic (and the languages
of commerce) |
French
(commerce) |
|
Uganda |
English (used in courts of law and by most newspapers and some radio
broadcasts) |
Ganda
(Luganda; most widely used of the Niger-Congo languages, preferred for
native language publications), other Niger-Congo languages, Nilo-Saharan
languages, Swahili, Arabic |
| Western Sahara |
|
Hassaniya Arabic,
Moroccan Arabic |
|
Zambia |
English |
major
vernaculars: Bemba, Kaonda, Lozi, Lunda, Luvale, Nyanja, Tonga, and about 70
other indigenous languages. |
| Zimbabwe |
English |
Chishona (Shona),
Sindebele (Ndebele), numerous but minor tribal dialects like: Sotho and
Nambya, Shangani, Venda, Chewa, Nyanja, and Tonga. |
Geographical Facts
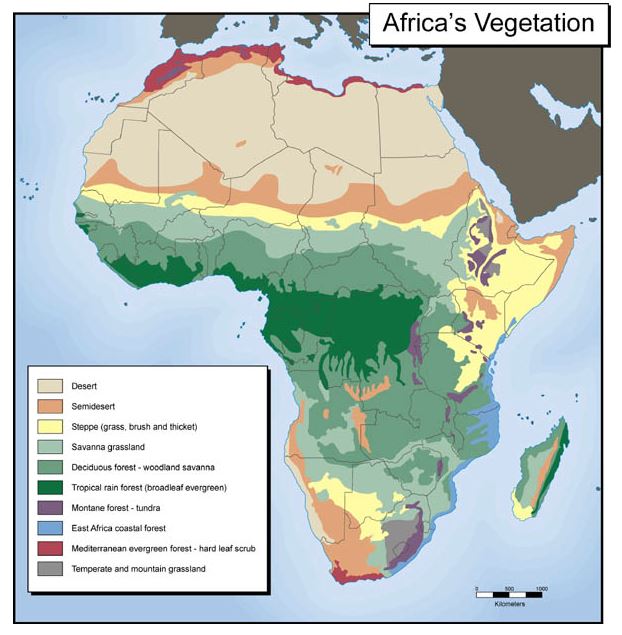
Africa, second-largest of the Earth's seven continents -
Largest Country
Sudan, Republic of, republic in north-eastern Africa, the largest country
of the African continent. Sudan has a total area of 2,505,800 sq km
(967,490 sq mi).
Smallest Country
The smallest African country is The Seychelles covering an area of 453 sq
km but Gambia is the smallest of the mainland African states, covering an
area of 11,300 sq km (4,363 sq mi).
Largest City
Egypt's capital city, Cairo, is the largest city in Africa with an
estimated 9.2 million population
Highest Point
Mount Kilimanjaro - Uhuru Point - (5895m/19,340 ft) in Tanzania
Lowest Point
the lowest is Lake 'Asal (153 m/502 ft below sea level) in Djibouti
Northernmost tip
is Cape Blanc (Ra's al Abyad;) in Tunisia
Southernmost tip
is Cape Agulhas in South Africa
Largest Lake
Lake Victoria is the largest lake in Africa and the is the world's
second-largest freshwater lake - covering an area of 69,490 sq km (26,830
sq mi) and lies 1,130 m (3,720 ft) above sea level. Its greatest known
depth is 82 m (270 ft).
Deepest Lake
Lake Tanganyika is the deepest lake in Africa reaching at its greatest
depth is 1,436 m (4,710 ft), making it the second deepest freshwater lake
in the world after Lake Baikal.
Longest River
The River Nile drains north-eastern Africa, and, at 6,650 km (4,132
miles), is the longest river in Africa and in the world. It is formed from
the Blue Nile, which originates at Lake Tana in Ethiopia, and the White
Nile, which originates at Lake Victoria.
The Great Africa Rift Valley
The Rift Valley extends more than 4,830 km (3,000 mi) from Syria in
south-western Asia to Mozambique in south-eastern Africa. The width of the
valley ranges from a few miles to more than 160 km (100 mi). In eastern
Africa, the valley splits into two branches: the Eastern Rift and the
Western Rift
The fault in which the Rift sits is still moving: the western side of the
rift is pulling away from the eastern ridge at about 6 mm per year, while
in the south it is moving together at a rate of 2 mm per year.
Lake Malawi
Lake Malawi contains the largest number of fish species of any lake in the
world, probably over 500 from ten families. Particularly noteworthy are
the Cichlidae, of which all but five of over 400 species are endemic to
Lake Malawi. The lake contains 30% of all known cichlid species. Of
particular interest is the 'mbuna' rock fish.
Namib Desert
The Namib is the world's oldest desert, and the only desert in Africa
inhabited by elephant, rhino, giraffe and lion
Namibia - Fish River Canyon
The Fish River canyon is the second largest canyon in the world.
The Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert is expanding southwards at an average of 0.8 km (½
mile) a month
sources: CIA World Fact Book, United Nations, U.S. Department of State |






