|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
Islamic Republic of Afghanistan
Flag : three equal vertical bands of black (hoist side), red, and green, with the national emblem in white centered on the red band and slightly overlapping the other two bands; the center of the emblem features a mosque with pulpit and flags on either side, below the mosque are numerals for the solar year 1298 (1919 in the Gregorian calendar, the year of Afghan independence from the UK); this central image is circled by a border consisting of sheaves of wheat on the left and right, in the upper-center is an Arabic inscription of the Shahada (Muslim creed) below which are rays of the rising sun over the Takbir (Arabic expression meaning "God is great"), and at bottom center is a scroll bearing the name Afghanistan
Ahmad Shah DURRANI unified the Pashtun tribes and founded Afghanistan in 1747. The country served as a buffer between the British and Russian empires until it won independence from notional British control in 1919. A brief experiment in democracy ended in a 1973 coup and a 1978 Communist counter-coup. The Soviet Union invaded in 1979 to support the tottering Afghan Communist regime, but withdrew 10 years later under relentless pressure by internationally supported anti-Communist mujahedin rebels. A civil war between mujahedin factions erupted following the 1992 fall of the Communist regime. The Taliban, a hardline Pakistani-sponsored movement that emerged in 1994 to end the country's civil war and anarchy, seized Kabul in 1996 and most of the country outside of opposition Northern Alliance strongholds by 1998.
Following the 11 September 2001 terrorist attacks, a US, Allied, and Northern Alliance military action toppled the Taliban for sheltering Osama Bin Ladin. A UN-sponsored Bonn Conference in 2001 established a process for political reconstruction that included the adoption of a new constitution, a presidential election in 2004, and National Assembly elections in 2005. In December 2004, Hamid KARZAI became the first democratically elected president of Afghanistan and was reelected in August 2009. In February 2020, the United States and the Taliban signed the “US-Taliban Agreement,” which contained commitments by the United States related to the withdrawal from Afghanistan of military forces of the United States, its allies, and Coalition partners, as well as commitments by the Taliban related to counterterrorism, among other topics. Following a US drawdown of virtually all its troops, a summer 2021 Taliban offensive quickly overran the country and the Taliban took over Kabul in August of 2021.
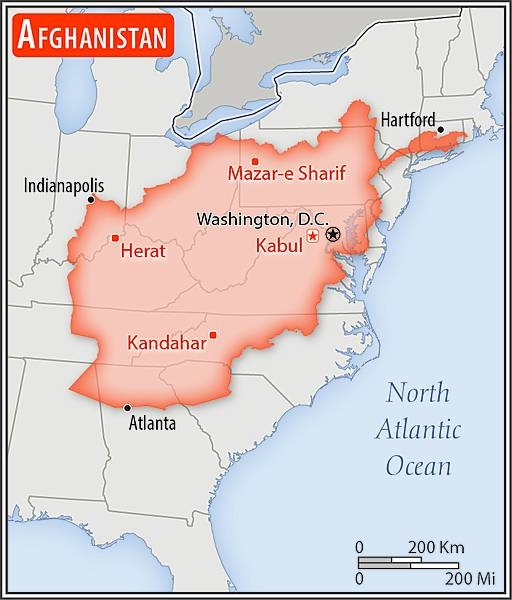
almost six times the size of Virginia; slightly smaller than Texas
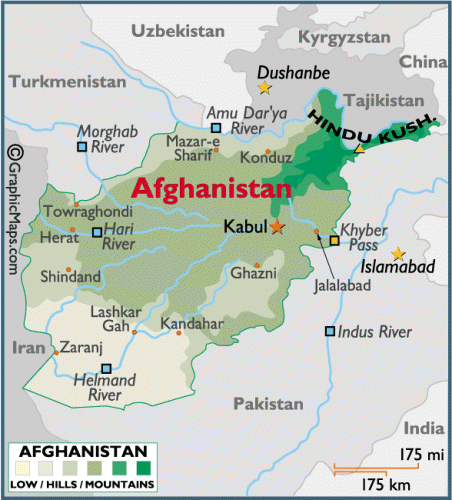
About the size of the U.S. State of Texas, most of Afghanistan is a rugged, inhospitable mountainous landscape. More than 50% of the total land area lies above 6,500 ft. (2,000 m). It all culminates in the high peaks of the Hindu Kush, where extensions of the Pamir Mountains, Karakorum Mountains and the Himalayas all come together. In the north a fertile plain fronts the Anu Dar'ya River. In the south, below the mountains, rolling desert and scattered salt flats cover the land. Afghanistan is drained by numerous rivers; significant ones include the Amu Dar'ya, Hari, Helmand, and the Kabul - directly east of the capital city, flowing down into the Indus River in Pakistan. 34 provinces (velayat, singular - velayat); Badakhshan, Badghis, Baghlan, Balkh, Bamian, Daykondi, Farah, Faryab, Ghazni, Ghowr, Helmand, Herat, Jowzjan, Kabol, Kandahar, Kapisa, Khowst, Konar, Kondoz, Laghman, Lowgar, Nangarhar, Nimruz, Nurestan, Oruzgan, Paktia, Paktika, Panjshir, Parvan, Samangan, Sar-e Pol, Takhar, Vardak, Zabol World's largest producer of opium The world’s largest producer of illicit opiates but it is not a major supplier to the United States; 215,000 hectares of opium poppy cultivated in Afghanistan in 2019; also produces methamphetamine and cannabis products; one of the highest domestic substanc abuse rates in the world
Source: CIA Factbook, United Nations
In 1803, a German pharmacist, F.W. Sertürner isolated the main alkaloid of opium and named it morphine after Morpheus, the Greek god of dreams. Morphine was soon widely used for medical purposes in Europe and the U.S. But by the end of the century, addiction to the drug had become a problem. In 1898, while searching for a non-addictive substitute for morphine, Heinrick Dresser, working at the Bayer Laboratory in Germany, developed diacetylmorphine. Bayer marketed it under the brand name Heroin. The new drug, however, turned out to be up to ten times more potent than morphine.
Opium poppies may look like innocent flowers out of a painting by Henri Matisse, but deep within their pods lies a substance that can be processed into heroin, a highly addictive drug used by 13 million people worldwide. In wartorn Afghanistan, opium poppies can be grown easily and bring in much-needed cash. But growing poppies is just the start. Before poppy pods can hit the streets as "junk," "horse" or "smack" (or as their chemical cousins, opium and morphine), they must undergo a long and complicated refining process.
Papaver somniferum, one
of the few species of poppy that produces opium, is an annual plant with a
growth cycle of 120 days. Farmers plant seeds, which range in color from white
to yellow to brown and gray, in shallow holes. Within six weeks a cabbage-like
plant emerges. It takes eight weeks for the poppy plant to grow about one to two
feet. Each poppy has one long primary stem with secondary stems called tillers.
As the plant continues to grow, a bud develops at the tip. After 90 days, the
bud blossoms into a flower with four petals in a variety of colors. The petals
fall away to reveal a green pod or ghozah that will continue to grow to
the size of an egg. Inside the pod is the ovary that produces opium. Opium,
which contains over 50 types of alkaloids including codeine and morphine, is
only produced during the ten to 12 day period when the pod is ripening. Once the
pod reaches maturity, the alkaloids in the opium are no longer made.
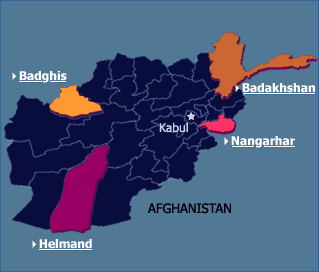
Areas In Afghanistan where opium is grown
credit: PBS, CIA,BBC |